Bioenergy
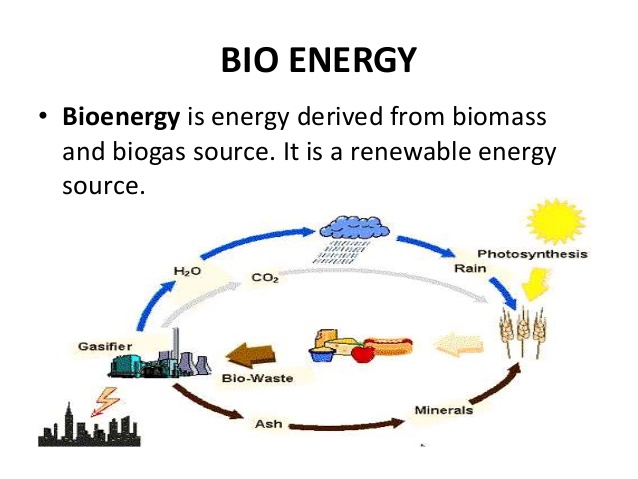
Biomass (any organic material) is considered a sustainable energy resource because it is a product of organic processes which naturally regenerate at a rapid cycle. Biomass can be combusted directly as a solid fuel or converted to liquid or gas biofuels. These biofuels can be used in either a combustion engine (conversion to mechanical energy) or in a fuel cell (conversion to electrical energy). Bio energy technologies are the processes and mechanisms that convert biomass into energy sources (biofuels). The processing technologies for biofuels depend on the kind of feedstock (biomass) and the type of biofuel derived from it. Given the several types of biofuels and the large array of potential feedstocks, there are many technological processes and pathways that are used for biofuels production. Biogas is created through the breakdown of any organic material (biomass) in an Oxygen-poor environment. The resulting gas by-product is mostly Methane and Carbon dioxide. Biogas is similar in composition to conventional natural gas and as such can be compressed or fed into a municipal gas grid. It can be used for many different purposes including cooking, heating, lighting, transportation, and electricity production.

